Produkte
Inspiration
Videos empfehlen Erfahren Sie, wie andere Nutzer Prezi Video verwenden, um ihr Publikum zu fesseln. Wiederverwendbare Präsentationen Durchstöbern Sie einige unserer beliebtesten Präsentationen und kopieren Sie diese, um sie als Vorlagen zu verwenden. Wiederverwendbare Infografiken Passen Sie den Inhalt dieser Infografiken an, um Ihre eigenen Kunstwerke zu schaffen. Präsentationsvorlagen Verschaffen Sie sich einen großen Vorsprung bei der Erstellung Ihrer eigenen Videos, Präsentationen oder Infografiken.Lösungen
Business
Für Marketing Erstellen Sie effektive, mit Ihrem individuellen Branding versehene Marketing-Botschaften, die jedes Publikum fesseln werden. Für Sales Erfahren Sie, wie die Beigabe von etwas Persönlichkeit in Ihre Sales-Botschaft Ihre Kundenbeziehungen verbessert. Fürs Personalwesen Machen Sie wichtige Materialien mit Prezi interessanter und einprägsamer.Ressourcen
Lernen
Produkt-Tutorials Werden Sie zu einem Prezi-Meister, indem Sie diese kurzen und einfach zu folgenden Videos ansehen. Präsentationstipps Buchen Sie einen Termin mit einem erfahrenen Prezi-Trainer, um Ihr Team von der Masse abzuheben. Bildungsressourcen Ein Sammlung pädagogischer Ressourcen und Best PracticesVerbinden
Webinare Sie benötigen Hilfe mit einer Präsentation, einem Video oder einer Grafik? Sprechen Sie noch heute mit einem Experten. Prezi-Blog Lesen Sie aktuelle Neuigkeiten und Tipps von unseren internen und Branchenexperten. Prezi-Nachrichtenzentrale Lernen Sie von Experten, Influencern und Vordenkern in unseren Webinaren und Foren.
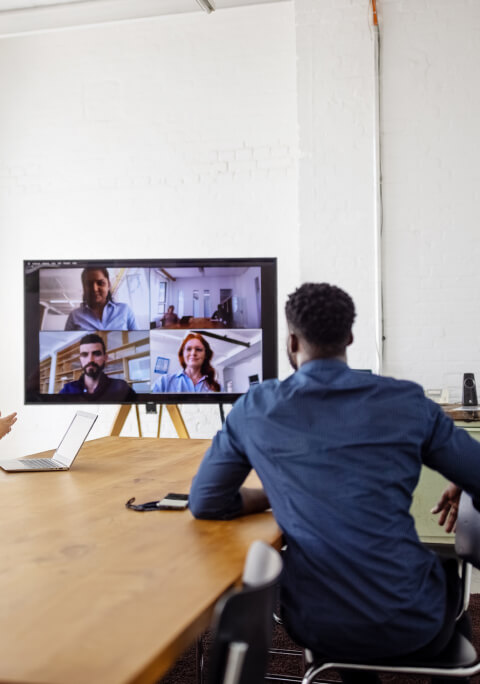
Erstellen Sie bewegliche, zoomende Präsentationen, die Aufmerksamkeit erzielen und aufrecht erhalten

Erscheinen Sie direkt neben Ihren Inhalten, während Sie vor Ihrem Publikum präsentieren.
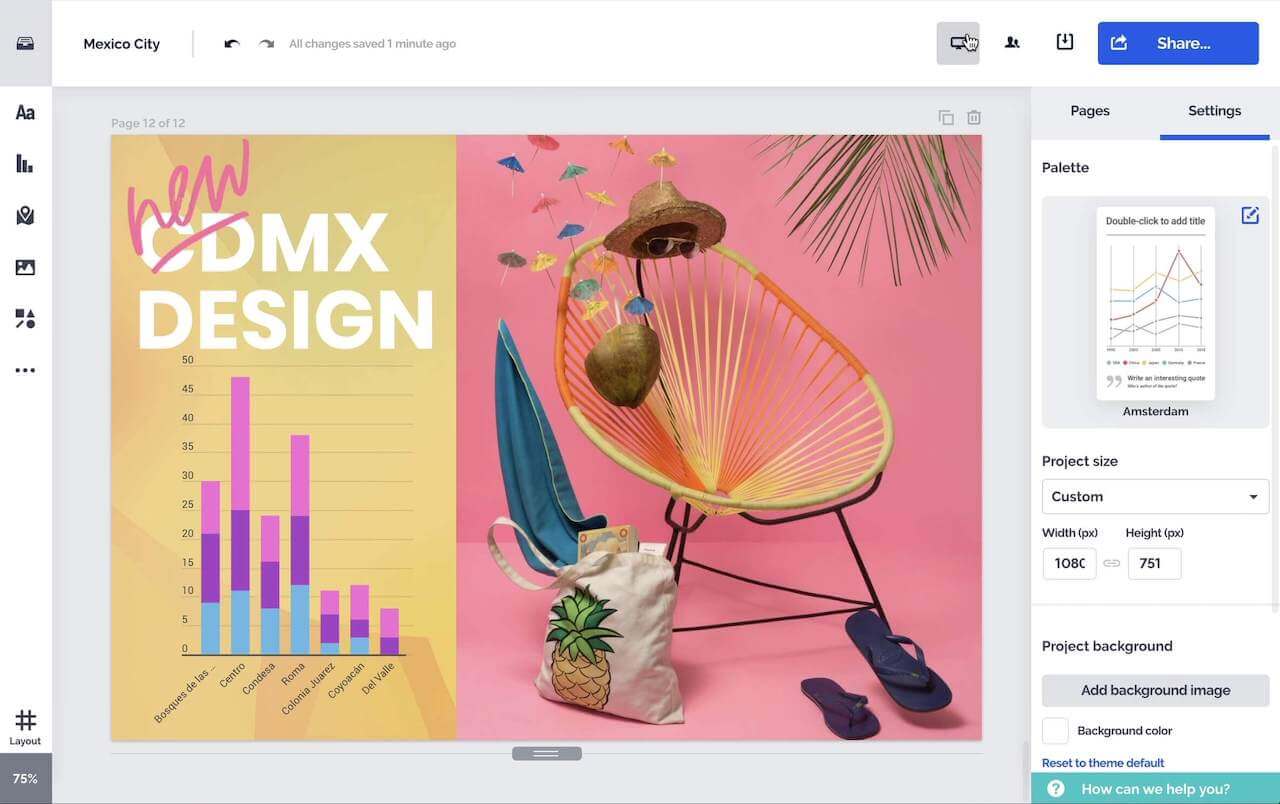
Erstellen Sie attraktive interaktive Diagramme, Berichte, Karten, Infografiken und mehr.





