Memory card
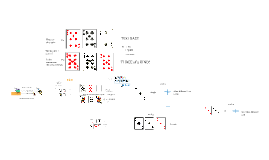
Transcript: Target Market Where product makes. Price of our product. DDR6 256-pin 86000 Warning!! If looking for customer service call this number :***-***-**** Products A/S Service last for 6 month (half year). Other problem than RAM does not accepted. Our target Market is 20~30 year old people, because they are most common computer users, also they are looking for computer parts so they can build their own computer. Our product changes if there is error or broken until 2 weeks from the day you bought. Our product is only works on DDR6 Memory card slot, problem of other than DDR6 does not accepted for repair. If computer detect less than 80,000 GB, check computer operation system, some of operation system does not support to 80,000 GB. system requirement : Windows 10 500 GB Hard drive Main board (mother board) that supports DDR6 Our memory card price is going to be $500 (not including tax), DD6 256-pin memory card has been just has been released for selling. DDR6 256-pin 86000 Memory card Our biggest Competitor Memory card also known as RAM is the machine that support computer to send information hard drive to CPU. Memory card electronic use age Our plan is to make good product as possible, but most importantly do advertisement as best as we can. Most of the sellers selling their stuff by advertisement that they made. even though other product is better than those product. Plan of our product DDR6 uses 0.2 V, using electronic less, also faster than before. Importance of our product DDR6 got 256-pin, 0.5mm smaller, and minimum speed of 23.6GT/s, maximum speed of 100.2 GT/s. 80,000GB of memory space. Our biggest competitor is Intel, because they are most advanced hardware developer. It has fast delivery but, they have bad place that they making our stuff, if its needed we will make at other places. Our product will be made in China, because they are good to make most of electronics, and they could make more than they make if it is needed. Our company want to be better and wants to people use our product.