Decision Making Flow Chart
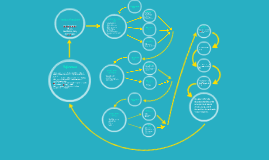
Transcript: School Level Decision Making Additional graduation requirements School budgets Dispersment of funding Bargain with teacher unions Funding of educators School policies Curriculum requirements Administration District Level Fletcher, A. (2006). SoundOut. Retrieved from http:// www.soundout.org/howdecisions.html It is not always obvious who makes decisions related to education. However, it is imperative to understand decision making pathways in order to affect school improvement and change (Fletcher, 2006 ). This chart represents who may become involved in decision making at the state, district, and school levels, and the roles and responsibilities included. Board of Education This position may be elected or appointed, and the individual can work with the state school board, the governor, or independently. This person implements rules, regulations, and budgets. District School Board References District Administration The school board is made up of elected officials who get recommendations from the public and the superintendent. They set the budget and agenda for schools, assign students to schools, make rules and policies, and set learning standards. Decision Making Flow Chart Laura Nevenner EDL/535 February 17, 2014 Melissa Connors Provide leadership Publicly represent school Mediate conflicts Interact with district, state, and federal authorities Authorize budgeting Guide student activities Participate on special committees Fletcher, A. (2006). SoundOut. Retrieved from http:// www.soundout.org/howdecisions.html Schimmel, D., Fischer, L., & Stellman, L. R. (2008). School law: What every educator should know a user- friendly guide. Boston, MA: Pearson Education, Inc. School Level Teachers References District Superintendent District Level Decision Making Conclusion Teacher Certification Graduation Requirements State Mandated Testing Procedures School and District Accreditation This elected group of officials oversees schools and ensures that the state adheres to federal rules and regulations. Policies set by the school board are requirements for all public schools. State Level This group can include principals, assistant principals, and school counselors. These are the leaders of the school. Introduction State Education Leader/Superintendent The district administration determines funding, rules, and regulations for the schools within their district. State Level Decision Making Teacher leaders and teachers make decions ding curriculum, committees, and classroom and behavior management. State and Regional Administration These people administer federal and state programs to meet school needs. They also provide professional development, administrative guidance, and funding to districts and schools. The district leader is responsible for all schools within a district. They act as the figurehead and authority of all education related issues. Educational decisions are made by state officials, district administration, and school officials. All of the decision makers have a governing body that helps guide the and protect the schools. Large decisions can be made at multiple levels and in or out of the school. Smaller decisions are usually made within the individual school. When stakeholders understand how, where, when, and why decisions are made, they can beging to influence decision making changes (Schimmel, Fischer, & Stellman, 2008).