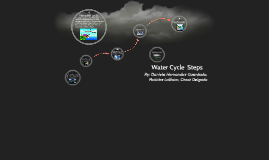
Water Cycle Steps
Transcript: Water Cycle Steps Precipitation is when rain,snow,sleet, or hail fall to the groud from the clouds. Precipitation: The cycle of processes by which water circulates between the earth's oceans, atmosphere, and land, involving precipitation as rain and snow, drainage in streams and rivers, and return to the atmosphere by evaporation and transpiration. The changing of a liquid into a gas, often under the influence of heat (as in the boiling of water). Condensation is the change of water form its gas form into a liquid. This occurs in the atmophere when warm air rises, cools and looses its capacity to hold water vapor Surface Runoff Accumaltion: Transpiration: The process by which moisture is carried through plants from roots to small pores on the underside of leaves, where it changes to vapor and is released to the atmosphere. Surface runoff is water, from rain, snowment, or other sources that flows over the land surface , and its major compoment of the water cycle . By: Daniela Hernandez-Guardado, Maurice Latham, Omar Delgado Condensation: The process in which water pools in large bodies (like oceans, seas and lakes). The water cycle: Evaporation: