Human Population
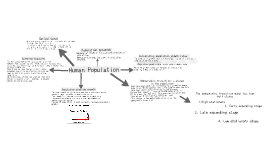
Transcript: geographic distribution density growth rate. Human Population Growth The human population cannot keep growing exponentially, because Earth & its resources are limited. Limiting Factors How Populations Grow Population Growth Human Population Growth Agriculture and industry made life easier and safer. Improved sanitation, medicine, and health care reduced the death rate and increased lifespans. At the same time, the birth rate remained high. This resulted in exponential population growth. Parasitism Predation A limiting factor is a factor that causes population growth to decrease. There are 2 types….. Limiting Factors How Populations Grow Exponential growth occurs when the individuals in a population reproduce at a constant rate. This type of population growth is characterized by a J -shaped curve. The size of the prey population determines the size of the predator population in an area. Population Growth Population density is the number of individuals per unit of area. This number can vary depending on the species and its ecosystem. Human Population Growth According to Thomas Malthus, war, famine, and disease would limit human population growth. Limits to Population Growth Population Growth The size of the human population tends to increase with time. About 500 years ago, the human population began growing more rapidly. This can be attributed to several factors… Predation The area inhabited by a population is known as its geographic distribution. There are 3 important characteristics of a population Populations can increase or decrease rapidly, depending on how many individuals are added to it or removed from it. Three factors that affect population sizes: Number of births Number of deaths Number of individuals entering or leaving the population. A limiting factor that depends on population size is called a density- dependent limiting factor. Emigration is the movement of individuals out of the population. Limiting Factors How Populations Grow Human Population Growth Population Carrying Capacity What types of factors? Age Structure Diagrams graph the numbers of people in different age groups in the population. Demographers can predict future growth using these models. These limiting factors only become limiting when the population density, or number of organisms per unit area, reaches a certain level. Four factors of this type are competition, predation, parasitism, and disease. Immigration is the movement of individuals into an area. Parasites also limit the population size. Parasites can range from microscopic bacteria to tapeworms that can measure 30 cm or more. Parasites take nutrients from their hosts, weakening them or causing disease or death. 5 species of birds in the same tree. What limiting factors would fish in this pond face? A population is a group of the same species living in the same area. Ex. Deer population Ex. Gray’s human population. Populations may also be controlled by predation, which involves a predator – prey relationship. Ex: Wolves and moose. When a population has abundant space and food, and is protected from predators and disease, the organisms will reproduce and the population size will increase. Population Ecology Population Growth The largest number of individuals that a given environment can support is called its carrying capacity Natural populations normally display logistic growth. Population Science Competition occurs when populations become crowded. Organisms compete with one another for food, water, space, sunlight and other essentials of life. Population Growth Human Population Growth How Populations Grow Density Independent….. Limiting Factors Density-Independent Factors affect all populations in similar ways, regardless of population size. These factors include human activities as well as severe natural conditions such as forest fires. Major upsets in the ecosystem can lead to long-term declines of certain populations. Competition may also occur between different species. This type of competition is a major force behind evolutionary change. Over time the species may evolve to be able to occupy separate niches. Populations Limiting Factors Population Science How Populations Grow Exponential growth of populations does not last very long. As resources become less available the growth of a population slows or stops. Logistic growth occurs after a period of exponential growth How are these organisms competing? A population will grow exponentially under ideal conditions with unlimited resources. The scientific study of human population is called demography. Demographers research birth rates death rates and age structure to help explain why some countries have higher growth rates than others. This type of population growth is characterized by an S-shaped curve. Examples of situations in which logistic growth is seen: When the birth rate and the death rate are the same. When the rate of immigration decreases and the rate of emigration increases.