Capnography
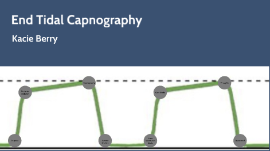
Transcript: Incorporating Capnography as a Standard of Care in High-Risk Patients Stakeholders The measurement of exhaled CO2 in partial pressure (35-45 mmHg) Wave patterns detecting partial pressure or ETCO2 concentration captured by capnogram Greg Miller, Medtronic Strategic Alliance Clinical Consultant, stresses importance of capnography nursing policy and algorithm in decreasing RRTs On N4, Phillips monitors not utilized to full potential Several RRTs observed since March 2016 related to respiratory decline. N4 equipped with eight Phillips modules Between ICU and DOU, 30 Phillips modules with ETCO2 capability. Capnography not utilized in every intubated patient Average use of ABG kit/month from Aug 2015-July 2016: 302, with 457 ABG kits used July 2016 Health Care Provider Education through In-Services Training is FREE and offered by Microstream 3 days out of the week in 30 minute training sessions Patient Education Algorithm for consistent use of capnography Implementation of Nursing Policy Marvelyn Ardoña, Brooke Colquhoun, Leila Coronado Patients, caregivers, patient advocacy groups Providers Taxpayers Employers Shareholders Policymakers Represents the partial pressure of CO2 at the end of expiration Measured by capnography using a CO2 nasal cannula SpO2 and ETCO2 ETCO2 Concentration of CO2 Measures ventilation, diffusion, and perfusion Detects hypoventilation immediately Represents an EARLY warning of changes Should be used in conjunction with a pulse oximeter Sample Algorithm Internal Evidence Population: Patients at risk for respiratory depression; those with ARDS, asthma, COPD, CHF, pneumonia, sleep apnea, bronchitis, receiving supplemental oxygen, and post-operative non-intubated patients utilizing PCA pumps for the deliverance of morphine or dilaudid Intervention: Implementation of capnography monitoring through utilization of Microstream O2/CO2 Nasal FilterLine/CapnoLine H O2 that supplies oxygen while measuring CO2 output Comparators: Number of RRTs called on the unit using capnography as a “gold standard” with previous RRT data without ETCO2 monitoring Outcomes: Early detection of increased CO2 levels prior to decline in oxygen saturation, decrease in RRT calls and hospital costs, change in clinical management, and an increase in quality of patient care and satisfaction VALBHS purchased 82 Phillips MX800s at a cost of $1,783/monitor (without accessories) for a total of $146,206 According to Elizabeth Roman-Ingleton, the Phillips module purchase for VISN 22 was a multimillion dollar contract Oral/Nasal FilterLine/Long Term costs: 100/pack: $1,595.00 Nasal Only 25/pack: $385.00 Average length of stay on med/surg unit: $1,500-1,800/day Cost of an RRT: ABG kit costs: 100/pack: $252.47 X-ray costs Transfer to a unit with higher acuity of care (ICU/DOU) No devoted RRT team! RTs, RNs, MDs, pharmacists must leave their work/patients Microstream Smart CapnoLine EVIDENCE SpO2 Risk Factors: Age >60 or >50 in the post-op setting Comorbidities: ARDS, asthma, COPD, CHF, pneumonia, sleep apnea, bronchitis, receiving supplemental oxygen, and post-operative non-intubated patients utilizing PCA pumps for the deliverance of Morphine or Dilaudid Christina DiBernardo, RN, CNL Ryan Mercer, Medtronic Monitoring Systems Specialist Greg Miller, Medtronic Strategic Alliance Clinical Consultant Santiago Constantino, SPD Distribution Elizabeth Roman-Ingleton, RN, CIS/ARK Coordinator ETCO2 Nasal Cannula Pulse Oximetry Capnography Set dates for Greg Miller to hold Education and Training for health care providers Communicate internal and external evidence and obtain feedback from leadership, clinicians, and stakeholders Development of Nursing Policy for Capnography in Non-intubated Patients at risk for Respiratory Depression Further development of Algorithm for implementation of capnography monitoring O2 saturation Measures oxygenation Detects hypoxia Represents a LATE sign for action Reading may be normal even if patient not breathing Should not be used alone when monitoring cardiopulmonary status If pulse oximetry measures the percentage of O2 in the arterial blood, why do we care about ETCO2 in respiratory depressed patients? Adult/Intermediate CO2 Oral/Nasal Sampling Set with O2 Tubing Recruitment of Team and Stakeholders The PICO Approach EVIDENCE-BASED PRACTICE QUESTION Interdisciplinary Team Microstream CapnoLine External Evidence Expert Opinion: According to the Joint Commission (2004-2010), 58% of opioid-related events resulting in death or permanent loss of function were the result of improper monitoring.” – American Society of Pain Management According to the Canadian Agency for Drug and Technology Health in their health technology assessment, “there was a lower likelihood of hypoxemia when patients were monitored with capnography.” VHA’s integrated product team recommended that patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) pumps with an integrated ETCO2 monitor is pump of choice because “use of this technology could have prevented