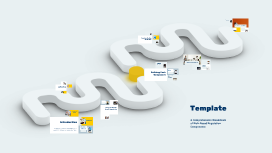
Blank Template
Transcript: Summary of Key Points The Compliance Delivery Framework ensures a structured approach to risk-based regulation. It highlights the importance of risk assessment, compliance monitoring, and continuous improvement as critical components to achieve regulatory goals. Conclusion and Next Steps This section encapsulates the primary insights from the Compliance Delivery Framework and outlines the path ahead for effective risk-based regulation. It emphasizes the necessity for ongoing improvement and stakeholder engagement in the compliance process. Call to Action for Stakeholders Future Directions for Compliance Delivery Stakeholders must actively participate in refining compliance processes. This includes providing feedback, investing in training, and committing to transparency to enhance the overall framework effectiveness. The evolution of technology will shape future compliance strategies. Emphasizing data analytics, real-time monitoring, and adaptive strategies will be crucial to keep pace with ever-changing regulatory landscapes. Steps to Operationalize the Framework Operationalizing the Compliance Delivery Framework involves defining clear objectives, establishing baseline assessments of current compliance levels, and outlining specific actions for risk management. Continuous evaluation and adjustments are necessary to align with evolving regulatory standards and organizational changes. Stakeholder Engagement Engaging stakeholders is vital to the successful implementation of the Compliance Delivery Framework. Developing a communication plan, involving stakeholders in planning discussions, and regularly seeking feedback fosters collaboration and ensures that diverse perspectives are considered, leading to enhanced compliance outcomes. Implementation Strategies Training and Capacity Building Effective implementation strategies are crucial for operationalizing the Compliance Delivery Framework, ensuring that risk-based regulation is not only theoretical but practically applied. This section delves into the necessary steps, stakeholder involvement, and training needed for successful execution. Training programs are essential to ensure that team members understand the Compliance Delivery Framework and their roles within it. Capacity-building initiatives should include workshops, e-learning modules, and ongoing support to empower employees, ensuring they are well-equipped to handle compliance challenges effectively. Common Implementation Challenges Challenges and Solutions Organizations frequently face challenges such as lack of resources, inadequate training, and resistance to change among staff. Additionally, misalignment of regulatory expectations can hinder effective implementation, leading to gaps in compliance outcomes. Understanding the obstacles in implementing a Compliance Delivery Framework is crucial for successful operationalization. By addressing common challenges, organizations can enhance their risk-based regulatory approaches effectively. Component 3: Continuous Improvement Lessons Learned from Case Studies Proposed Solutions Continuous improvement focuses on refining compliance processes through feedback loops and performance metrics. This iterative approach not only enhances the organization's compliance posture but also fosters a culture of proactive regulatory engagement, driving better outcomes over time. Case studies reveal that organizations implementing gradual changes yielded better compliance outcomes. Regular feedback loops and adapting to changing regulations proved essential in maintaining compliance and mitigating risks effectively. To overcome challenges, organizations should invest in comprehensive training programs and foster a culture of compliance among employees. Implementing robust communication channels and aligning expectations with regulators can also enhance the framework's effectiveness. Component 2: Compliance Monitoring Compliance monitoring involves continuous oversight of activities and processes to ensure adherence to established regulations. Utilizing technology and data analytics, organizations can track compliance in real-time, identify deviations, and implement corrective actions swiftly. Defining Each Component Component 1: Risk Assessment This section focuses on the crucial components of the Compliance Delivery Framework: risk assessment, compliance monitoring, and continuous improvement, providing a clear understanding of their roles and significance in operationalizing risk-based regulation. Risk assessment identifies potential compliance risks by evaluating various factors such as industry standards and historical data. This proactive approach allows organizations to prioritize risks and allocate resources effectively, ensuring regulatory obligations are met with optimal efficiency. Visual Representation of Framework The visual representation of the Compliance Delivery Framework illustrates the flow and interaction between its components. This graphic