Chronic Kidney Disease
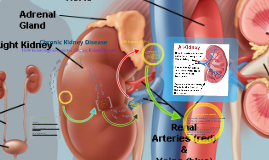
Transcript: A few risk factors for CKD are: Diabetes High blood pressure Obesity Smoking Identify risk factors for Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD). Identify ways to prevent CKD. Verbalize understanding of the consequences of CKD. Prevention begins with eliminating possible risk factors. Diabetes management and/or prevention Blood pressure management and/or preventing low or high blood pressure Maintain/achieve a healthy weight No smoking (Crockell, 2012; Curhan, 2014) Crockell, Y. J. (2012). Management of chronic kidney disease: An emphasis on delaying disease progression and treatment options. (cover story). Formulary, 47(6), 228-CV3. Curhan, G. (2014). BE KIND TO YOUR KIDNEYS. (Cover story). Nutrition Action Health Letter, 41(2), 1-6. dLifedotcom (2013). Ben On Dialysis. Retrieved from www.youtube.com Lewis, R. (2013). An overview of chronic kidney disease in older people. Nursing Older People, 25(10), 31-38. Reddenna, L., Basha, S., & Reddy, K. (2014). Dialysis Treatment: A Comprehensive Description. International Journal Of Pharmaceutical Research & Allied Sciences, 3(1), 1-13. Westwood, W. (2014). Preventing and Treating Kidney Disease. Retrieved from www.youtube.com Preventing CKD (Crockell, 2012; Curhan, 2014) By Samantha Costello, RN Discussion Risk Factors for CKD Questions? Comments? References 1. What are two risk factors for CKD? 2. What are two ways you can prevent CKD? 3. What are two undesirable consequences of CKD? GOAL! Goal: “Reduce new cases of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and its complications, disability, death, and economic costs” -Healthy People 2020 The Ultimate Consequence: See "Be Kind To Your Kidneys" handout, page number 3; "Why is kidney disease harmful?" (Curhan, 2014). Also see "What a Kidney Does" on the same page of the handout. If the kidneys fail due to end stage renal failure, all of these functions are compromised. Chronic Kidney Disease Objectives See short video (2:11): Consequences of CKD Watch this short video about one man's journey (4:19):